Chelated Magnesium Vs Magnesium Glycinate and Magnesium Glycinate are both highly absorbable forms of magnesium, with chelated magnesium being bound to amino acids for better absorption, while Magnesium Glycinate is a specific form of chelated magnesium bound to the amino acid glycine, known for its calming effects on the brain and body. Considering the various forms of magnesium supplements available today, it’s essential to understand the differences between chelated magnesium and Magnesium Glycinate.
Both are considered highly bioavailable, but each offers specific benefits for different individuals. By delving into the distinctive qualities of these two forms of magnesium, consumers can make an informed choice based on their individual health needs and goals. Understanding the unique properties of chelated magnesium and Magnesium Glycinate can help optimize the potential health benefits of magnesium supplementation.
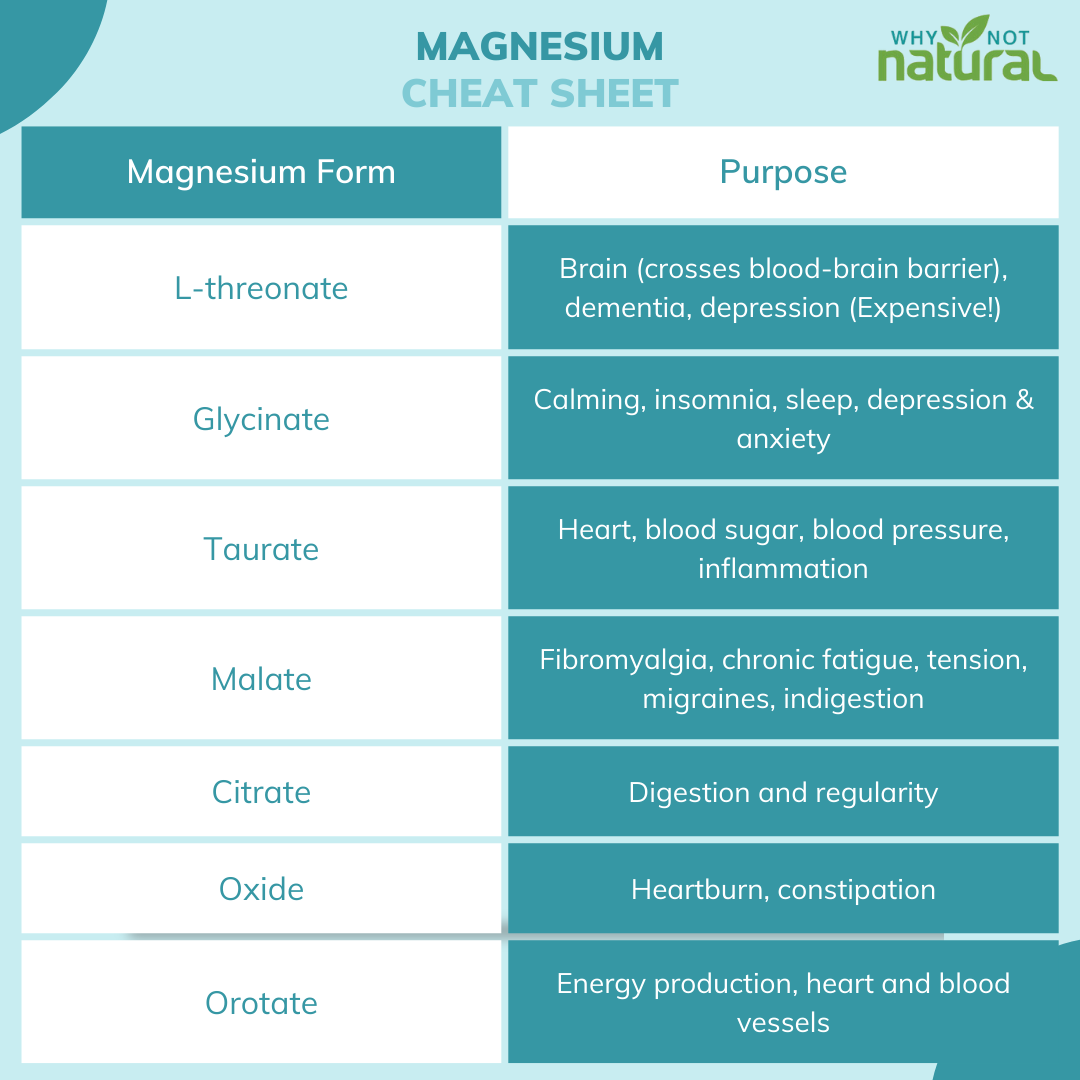
Credit: whynotnatural.com
Differences Between Chelated Magnesium And Magnesium Glycinate
Chelated magnesium and magnesium glycinate are two popular forms of magnesium supplements. While chelated magnesium is bound to amino acids for better absorption, magnesium glycinate is a compound of magnesium and glycine, offering high bioavailability and minimal laxative effect. Both forms provide distinct benefits for various health concerns.
Absorption
One of the key differences between chelated magnesium and magnesium glycinate lies in their absorption rates. Chelated magnesium refers to magnesium bound with amino acids, such as glycine, which enhances its absorption in the body. On the other hand, magnesium glycinate is a specific form of chelated magnesium in which the mineral is bound with the amino acid glycine. Due to this unique bond, magnesium glycinate is highly bioavailable, meaning it is readily absorbed and utilized by the body.
Bioavailability
Bioavailability plays a significant role in determining the effectiveness of magnesium supplementation. Chelated magnesium, as mentioned earlier, has greater bioavailability compared to other forms, including magnesium glycinate. This increased bioavailability ensures that a higher percentage of the magnesium in chelated form can be absorbed and utilized by the body, providing more benefits.
Tolerance
When it comes to tolerance, magnesium glycinate tends to be better tolerated by individuals compared to chelated magnesium. This is because the amino acid glycine helps to buffer the mineral’s potential laxative effect. However, it is important to note that everyone’s tolerance to magnesium may vary, and some individuals may still experience digestive discomfort with either form of supplementation.
Dosage
The recommended dosage for chelated magnesium and magnesium glycinate may also differ slightly. It is important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer or consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate dosage recommendations based on your specific needs. Typically, magnesium glycinate supplements contain a higher concentration of elemental magnesium compared to chelated magnesium supplements, allowing for smaller dosages to achieve the desired effect.
Side Effects
Both chelated magnesium and magnesium glycinate are generally considered safe for most individuals when taken within the recommended dosage range. Like every supplement, there is a chance for adverse effects, though. Common side effects of magnesium supplementation may include gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea or stomach cramps. It’s crucial to get medical help if you have any concerns or suffer from serious adverse effects.

Credit: www.amazon.com

Credit: whynotnatural.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Chelated Magnesium Vs Magnesium Glycinate
Is Chelated The Same As Glycinate?
Chelated refers to minerals bound to another molecule for better absorption, while glycinate specifically refers to minerals bound to glycine amino acid.
Why Is Chelated Magnesium Better?
Chelated magnesium is better because it is more easily absorbed and utilized by the body. It has higher bioavailability and is less likely to cause digestive discomfort. Chelated magnesium also helps with various health issues, such as muscle function, energy production, and bone health.
What Is The Difference Between Magnesium Glycinate And Regular Magnesium?
Magnesium glycinate is a type of magnesium supplement that is easily absorbed by the body, making it more effective. Regular magnesium may not be as easily absorbed, leading to potential digestive issues.
What Is The Best Type Of Magnesium To Take?
The best type of magnesium to take is magnesium citrate. It is easily absorbed by the body and helps with muscle relaxation, energy production, and overall health.
Conclusion
After comparing chelated magnesium and magnesium glycinate, it’s clear that both have unique benefits, making it vital to determine individual needs and preferences. When selecting a magnesium supplement, factors like bioavailability, absorption, and tolerability must be considered. Consulting a healthcare professional is key to selecting the best option.


